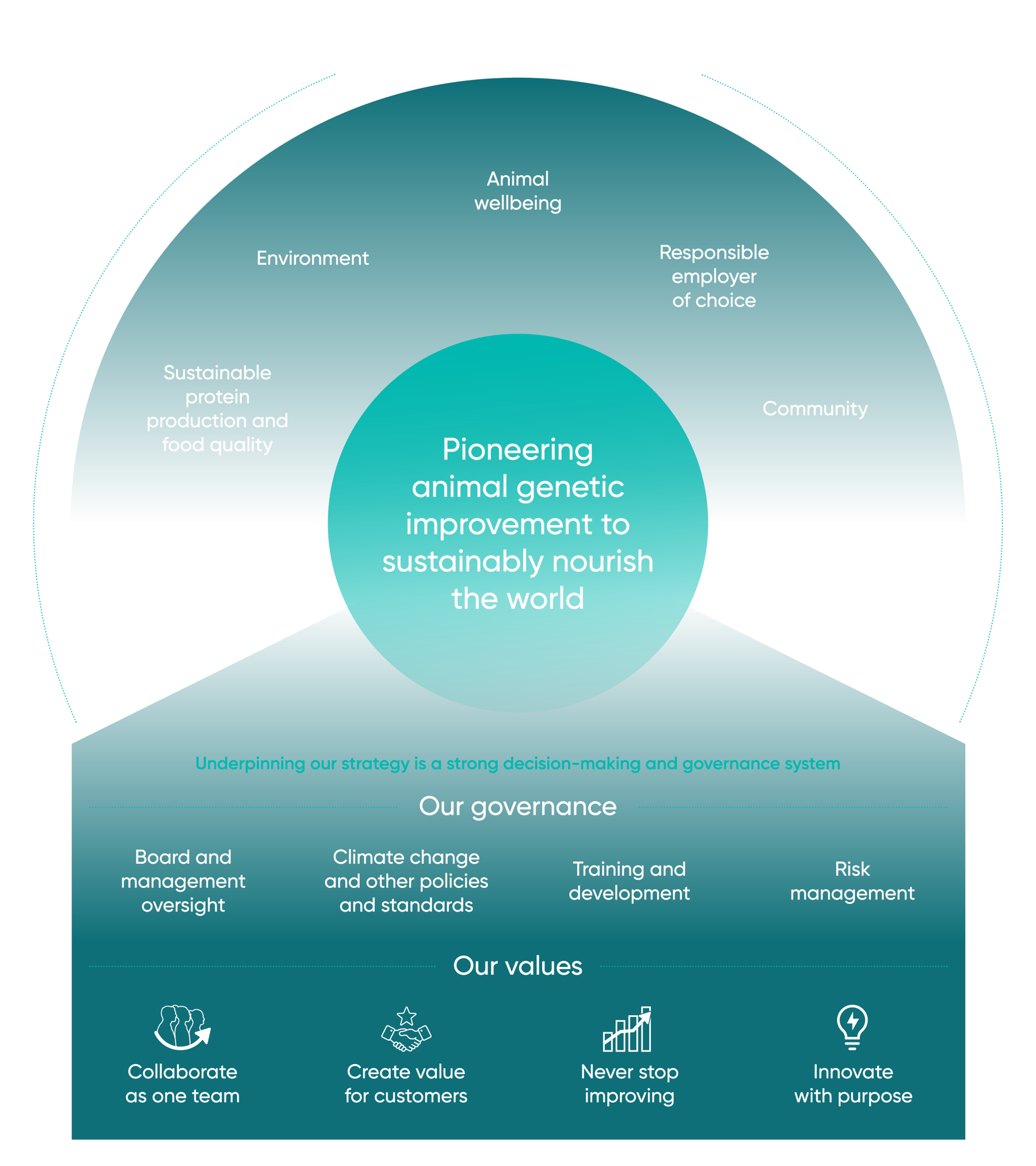
What could global dairying look like if we improved health, nutrition and genetics?
In one of our key markets and a showcase for our technologies, UK milk yields are 216% better than the global average, reflecting combined impacts of improved animal health, nutrition and genetics.
Applied to the 'global herd', the same level of production could be maintained using 181 million fewer cows. At US average yields (also a key Genus Market), the same level of output could be achieved using 200 million fewer cows.